|
|

|

|

|

|
|
In January-February 1991 an acoustic source lowered from a ship near Heard Island in the
southern Indian Ocean was used to transmit coded signals that were detected throughout
the world's oceans. This test was the Heard Island Feasibility Test. Click on the image
for a better view of the map.
|
The Heard Island Feasibility Test (HIFT) was an experiment conducted
in 1991 to test the ability of man-made acoustic signals to travel throughout the world's oceans. The experiment
was used to test engineering of acoustic sources and receivers for transglobal ranges, to study the nature of
acoustic signals recorded at great distances from their source, and as a preliminary test of the tool of long-range
acoustics for the purposes of measuring global oceanic climate change.
This web page documents the development of the HIFT idea, the science questions that
motivated the experiment, the engineering and organization required to achieve the global test,
and the conclusions and questions resulting from the experiment.
|

|
|
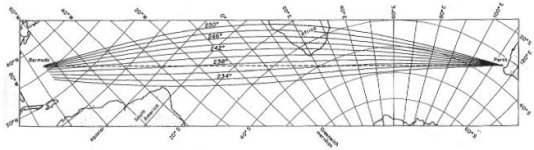
In 1960 the sounds from a sequence explosive charge detonated off Perth, Australia were
detected at Bermuda in the North Atlantic, about 19,820 km away. In the late 1980's, a question
arose concerning the travel times that were recorded and the acoustic path that was required to
give that travel time.
(The top banner of this page shows the Perth to Bermuda acoustic paths.)
Munk, O'Reilly, and Reid (1988) concluded that global acoustic transmissions are very sensitive to
oceanographic conditions. These considerations led to the notion that long-range acoustic transmissions might
be a sensitive measure of the ocean's climate.
|

|
|
The Perth test and the analysis of the properties of acoustics to account
for the observations raised the interesting notion of using the characteristics of
sound at very long ranges in the ocean to measure small changes in the average ocean
temperature. Such measurements address the question of the warming of the oceans in
response to climate change. In contrast to the normal turbulent variability of the ocean,
changes in the ocean's average temperature as a result of climate change are expected to be
tiny - about 0.005°C per year at 1000 m depth is a nominal expectation. Measuring such small
changes conventionally is difficult, while the acoustical approach appears to be ideally
suited for the measurement.
Walter Munk therefore conjectured that long-range acoustics could provide a direct
way to measure oceanic climate change. The Heard Island Feasibility Test was designed to test
the ability of man-made sounds to be detected and deciphered at a location on the other side
of the world.
|

|
|
The basic goals of HIFT were quite simple: Can controlled, man-made acoustic signals
travel antipodal distances over the world's oceans? If those signals are detected, can
resolvable information be extracted from them such that accurate travel times can be obtained
for the measurement of temperature? Prior to HIFT, the various estimations of the attenuation
of acoustic energy were widely varying, so that the detection of the transmissions at great
distances was not at all assured.
|

|
|
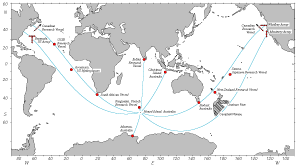
The HIFT experiment was organized by a collaboration between the Scripps Institution
of Oceanography (Walter Munk), the Applied Physics Laboratory, University of Washington (Bob Spindel),
the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (Art Baggeroer) and the University of
Michigan (Ted Birdsall). This group enlisted the help of a larger international collaboration of
researchers willing to deploy acoustic receivers at widely varying and
key locations throughout the worlds oceans. The HIFT collaboration was enthusiastic and
multinational. Small, portable hydrophone systems (acoustic receivers) were developed and sent to
several key locations, while other collaborators used sophisticated ship-towed hydrophone arrays.
As a result of concerns that arose about the effect the acoustic transmissions may
have on the marine life around Heard Island, whales in particular, the HIFT collaboration grew to
encompass a contingent of marine biologists who were to observe and monitor marine life during the
experiment. The biological component of HIFT was conducted on board the M/V Amy Chouest, a sister
ship to the M/V Cory Chouest.
|

|
|
Engineering efforts for the HIFT experiment consisted of a number of components. The
acoustic sources are specially designed for high power and low frequency. The ship used
to conduct the experiment had to be robust enough to withstand the extreme weather of
the Southern Ocean. A variety of hydrophone arrays, the acoustic receivers, were used
to study the acoustical signals. Finally, extensive research on signal processing was
conducted, both to craft an optimal collection of signals to transmit from the source and
to optimally process the received signals to glean the most information possible from them.
|

|
|
The Heard Island experiment occurred in January-February 1991, with the M/V's Cory
Choust and Amy Chouest departing from Perth Australia on 9 January. The plan was to begin
the transmissions of the experiment on Australia Day, 26 January, although the ships departed port
prior to obtaining the required permits. Permits were required as a consequence of
the marine mammal controversy that the experiment engendered. The permits were obtained
at the last minute, but the weather did not cooperate...
|

|
|
While HIFT demonstrated that global acoustic transmissions were possible,
its five day duration and complicated acoustic signals precluded any use of the data for
determining anything of the ocean's climate state. In addition, work with numerical ocean
models showed that multi-basin measurements were less desireable than basin-scale
measurements, which are more suited to the expected patterns of climate change. As a
follow on of HIFT and other experiments, a decade-long experiment called the Acoustic
Thermometry of Ocean Climate (ATOC) was conducted from 1996–2006 in the eastern
North Pacific. This experiment ran into similar problems with marine mammal concerns,
but after considerable negotiation permits were obtained, the experiment proceeded, and
a decade's worth of acoustic data were obtained giving basin-wide average measurements
of the seasonal and interannual temperature variations.
|
|