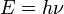Emission of Photon
Whatever the source of excitation the key step is when the electron jumps from an excited state back to the ground state and in the process releases a photon.
This is done with the exe latex equation editor
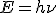
this is done with flash
The Planck constant (denoted h), also called Planck's constant, is a physical constant used to describe the sizes of quanta in quantum mechanics. It is named after Max Planck, one of the founders of quantum theory. The Planck constant is the proportionality constant between energy (E) of a photon and the frequency of its associated electromagnetic wave (ν). This relation between the energy and frequency is called the Planck relation.
The Planck constant has dimensions of energy multiplied by time, which are also the dimensions of action. In SI units, the Planck constant is expressed in joule seconds (J s). The dimensions may also be written as momentum multiplied by distance (N m s), which are also the dimensions of angular momentum.
The value of the Planck constant is:[1]
- h = 6.626 068 96(33)×10−34 J s = 4.135 667 33(10)×10−15 eV s
This article is licensed under the GNU Free Documentation License. It uses material from the article "planks constant".